Cardiac Arrythmias and ECG Guidelines
Understanding the ECG Strip
Arrhythmia
|
Heart Rate
(bpm)
|
Rhythm
|
P wave
|
PR Interval
|
QRS Complex
|
Normal Sinus Rhythm
|
60-100
|
Regular
|
Normal
|
Normal
|
Normal
|
Sinus Tachycardia
|
100-180
|
Regular
|
Normal;
may be peaked
|
Normal
|
Normal
|
Sinus Bradycardia
|
<60
|
Regular
|
Precedes
QRS
|
Normal
|
Normal
|
Premature Atrial Complex
|
Dependent
on rhythm
|
Irregular
due to premature complexes
|
Same,
different or absent
|
0.12-0.20
|
1:1
|
Atrial Tachycardia
|
160-250
|
Regular
|
Normal
|
0.08 sec
|
Normal
|
Atrial Flutter
|
60-150
|
Usually
regular, may be irregular
|
Atrial
flutter waves
|
Normal
|
|
60-180
|
Irregular
|
Absent |
None
|
Normal
|
|
Present
or Absent
|
Irregular
|
normal
|
Not
measurable
|
Distorted
>0.12
sec
|
|
110-250
|
Regular
|
Present
or Absent,
No
relation to QRS complexes
|
None
|
Abnormal
>0.12
sec
|
|
Ventricular Fibrillation
|
None
|
None
|
Present
or Absent
|
None
|
Ventricular
fibrillation waves
|
Accelerated Idioventricular rhythm
|
40-100
|
Regular
|
Present
or Absent,
No
relation to QRS complexes
|
None
|
Abnormal
>0.12
sec
|
<40
|
Regular
|
Present
or Absent,
No
relation to QRS complexes
|
None
|
Abnormal
>0.12
sec
|
|
None
|
None
|
Present
or Absent
|
None
|
None
|
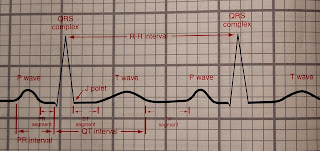
ECG Strip
0.04 sec – small square
0.20 sec - large square
WAVES
|
Definition
|
P wave
|
Represents depolarization of the right and left atria
|
QRS complex
|
Represents depolarization of the right and left ventricles
|
T wave
|
Represents ventricular repolarization
|
U wave
|
Probably represents the final stage of repolarization of the
ventricles
|
PR interval
|
Represents the time of progression of the electrical impulse from the
SA Node, an ectopic pacemaker in the atria, or an ectopic or escape pacemaker
in the AV junction, through the entire electrical conduction system of the
heart ventricular myocardium, including the depolarization of the atria
|
QT interval
|
Represents the time between the onset of depolarization and the termination of repolarization of
the ventricles
|
R-R interval
|
Represents the time between two successive ventricular
depolarizations
|
ST segment
|
Represents the early part of repolarization of the right and left
ventricles
|
PR segment
|
Represents the time of progression of the electrical impulse from the
AV node through the bundle of His, bundle branches, and Purkinje network to
the ventricular myocardium
|
TP segment
|
Is the interval between two successive P-QRST complexes, during which
electrical activity of the heart is absent
|
Basic
Dysrhythmias, Robert J. Huszar, Revised Third Edition
Basic Heart Drugs:
β-Blockers "olol"- such as metoprolol slow conduction of impulses through the AV node and decrease the heart rate.
-Propranolol (inderal ):
Side effect: Audible expiratory wheezes may indicate a serious adverse reaction, bronchospasm.
Calcium channel blockers "dipine" - primarily decrease spasm in cerebral blood vessels
Atropine sulfate will further increase the heart rate and will further decrease the cardiac output.
Lidocaine is useful in suppressing ventricular dysrhythmias.
Warfarin (Coumadin) is administered to clients with atrial fibrillation to prevent clots from forming in the atria it will have no effect in decreasing the ventricular rate or restoring normal sinus rhythm.
Nitroglycerin is a vasodilator and will lower the blood pressure.
Basic Heart Drugs:
β-Blockers "olol"- such as metoprolol slow conduction of impulses through the AV node and decrease the heart rate.
-Propranolol (inderal ):
Side effect: Audible expiratory wheezes may indicate a serious adverse reaction, bronchospasm.
Calcium channel blockers "dipine" - primarily decrease spasm in cerebral blood vessels
Atropine sulfate will further increase the heart rate and will further decrease the cardiac output.
Lidocaine is useful in suppressing ventricular dysrhythmias.
Warfarin (Coumadin) is administered to clients with atrial fibrillation to prevent clots from forming in the atria it will have no effect in decreasing the ventricular rate or restoring normal sinus rhythm.
Nitroglycerin is a vasodilator and will lower the blood pressure.







Comments
Post a Comment